In India, Packing Credit Against LC is a pre-shipment finance facility that helps exporters meet working capital requirements before shipment. It is a short-term loan sanctioned by banks against a confirmed Letter of Credit (LC) or a firm export order.
The bank releases funds in advance, enabling the exporter to purchase raw materials, process goods, pay for labour, and handle packaging and logistics. Once the export proceeds are realized, the loan is repaid automatically.
How it Works in Practice:
Suppose an exporter in Mumbai receives a confirmed LC worth ₹1 crore from a buyer in Singapore. The exporter’s bank can extend up to 90% of the LC value as packing credit. The exporter uses the funds to full-fill the order, and once the buyer’s payment is received under the LC, the bank adjusts the loan.
Key Features of Packing Credit in Export:
- Purpose: To finance pre-shipment expenses (materials, wages, logistics).
- Tenure: Up to 180 days, extendable with bank approval.
- Interest Rate: Concessional under RBI’s export credit norms.
- Mode: Can be issued in INR or Foreign Currency (PCFC).
- Repayment: Through export realization.
- Security: Supported by LC or firm export order.
Packing Credit is one of the most preferred financing methods in international trade as it provides liquidity when exporters need it most — before shipment.
Table of Contents
Types of Packing Credit
Exporters can avail different types of Packing Credit Against LC in India, depending on their business model and order structure:
- Packing Credit Against LC: Loan backed by a confirmed LC from the buyer’s bank.
- Packing Credit Against Firm Order: Granted against a signed export purchase order.
- Running Account Packing Credit: Offered to regular exporters without order-specific limits.
- Red Clause LC: Allows pre-shipment advance before goods are dispatched.
- Back-to-Back LC: Issued when a trader uses one LC to open another in favor of their supplier.
Importance of Packing Credit
Packing Credit Against LC in India helps exporters maintain production efficiency and meet global deadlines.
Why it matters:
- Ensures smooth procurement and manufacturing flow.
- Reduces cash flow stress during the pre-shipment stage.
- Improves buyer trust due to timely delivery.
- Boosts India’s export competitiveness.
Banks also benefit from LCs as they minimize default risk through guaranteed buyer payments.
Eligibility Criteria for Export Packing Credit
Before approving Packing Credit Against LC, banks conduct due diligence on the exporter, the LC, and the transaction.
Exporter Eligibility:
- Must hold a valid IEC (Importer Exporter Code) issued by DGFT.
- Engaged in export of goods/services under India’s Foreign Trade Policy (FTP).
- Maintain a satisfactory credit history and active current account.
- Must comply with KYC and AML norms.
Transaction Eligibility:
- Must possess a confirmed and irrevocable LC or a firm export order.
- The LC should be issued by a recognized, reputable (prime) bank.
- Export order must clearly mention terms, shipment schedule, and product details.
Documents Required:
- Copy of LC or export order.
- Proforma invoice and shipment details.
- PAN, GSTIN, and IEC documents.
- Audited financial statements.
- Bank statements showing turnover and credit history.
Banks may ask for collateral or margin depending on credit risk, but LC-backed credits are often self-secured due to LC assurance.
Pre-Shipment Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC)
RBI allows exporters to avail Packing Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC) to reduce borrowing costs.
Benefits of PCFC:
- Lower interest rates (linked to SOFR or LIBOR benchmarks).
- No currency conversion risk for foreign-currency transactions.
- Enhances exporter competitiveness globally.
Repayment is done once export proceeds are realized in foreign currency, and the PCFC account is adjusted
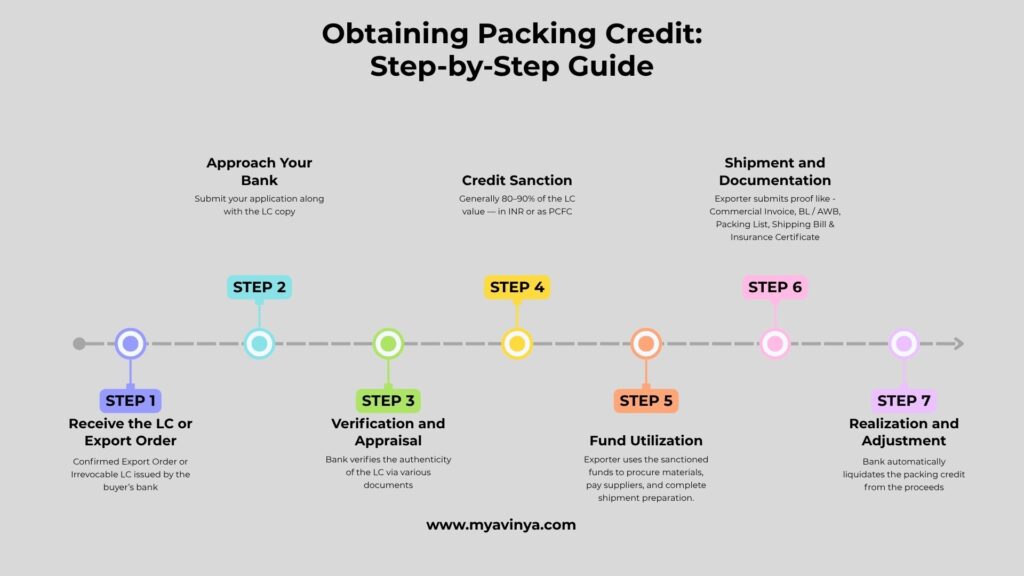
Obtaining Packing Credit: Step-by-Step Guide
Here’s how exporters can practically secure Packing Credit Against LC in India:
Step 1 – Receive the LC or Export Order
Start with a confirmed LC issued by the buyer’s bank. It serves as collateral for the loan.
Step 2 – Approach Your Bank
Submit your application along with the LC copy, proforma invoice, and estimated cost of export.
Step 3 – Verification and Appraisal
The bank verifies the authenticity of the LC via SWIFT, checks buyer reputation, and assesses the exporter’s credit record.
Step 4 – Credit Sanction
Once verified, the bank sanctions packing credit — generally 80–90% of the LC value — in INR or as PCFC.
Step 5 – Fund Utilization
The exporter uses the sanctioned funds to procure materials, pay suppliers, and complete shipment preparation.
Step 6 – Shipment and Documentation
After shipping, the exporter submits proof like:
- Commercial Invoice
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
- Packing List
- Shipping Bill & Insurance Certificate
Step 7 – Realization and Adjustment
When the buyer’s payment is received under the LC, the bank automatically liquidates the packing credit from the proceeds.
Exporter Tip: Track LC expiry and shipment dates carefully — any mismatch or delay can result in non-payment or higher interest.
Packing Credit vs Working Capital vs LC vs Cash Credit
| Feature | Packing Credit | Working Capital Loan | Letter of Credit (LC) | Cash Credit (CC) |
| Purpose | Pre-shipment finance | General business funding | Payment assurance | Business liquidity |
| Security | LC or export order | Stock & receivables | Buyer’s bank guarantee | Inventory |
| Tenure | Up to 180 days | 1 year or more | Until payment | Revolving |
| Repayment | Through export proceeds | Business revenue | As per LC | Rolling |
| Interest Rate | Lower (export credit rate) | Moderate | Not applicable | Higher |
Example of Packing Credit in Action
An exporter from Surat receives a $200,000 LC from a U.S. buyer.
Her bank verifies the LC via SWIFT and grants ₹1.5 crore as packing credit in INR.
The funds are used for procurement and production. Once shipment is complete and the buyer’s payment arrives, the bank deducts the loan and credits the remaining amount to her account.
Packing Credit for Deemed Exports
Exporters supplying goods to SEZs, EOUs, or projects under international funding can also avail Packing Credit Against LC in India under Deemed Export status.
This ensures domestic suppliers receive the same financial benefits as overseas exporters.
FAQ
Q. What is Packing Credit?
A. It’s a pre-shipment loan provided to exporters to finance production and shipping before receiving payment.
Q. Can I get Packing Credit without an LC?
A. Yes, if you have a confirmed export order from a reputed buyer.
Q. What is the repayment period?
A. Typically within 180 days, extendable to 270 days with approval.
Q. What is PCFC?
A. Pre-Shipment Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC) allows exporters to borrow in USD, EUR, etc., at lower rates.
Q. What documents are required?
A. LC copy, IEC, export order, business financials, and KYC details.
Q. Can new exporters apply?
A. Yes, but banks may sanction smaller limits initially based on experience and turnover.
Final Words
In 2025, Packing Credit Against LC in India remains an essential trade finance tool for exporters. It bridges the working capital gap between receiving an order and realizing payment.
By leveraging LC-backed finance, exporters can ensure timely delivery, maintain production flow, and strengthen global trade relationships.
Read next: Letter of Credit (LC) 2025 in India – Types & Importance
For detailed rules, refer to the RBI Master Direction on Export Credit (Do Follow link).
Disclaimer
This blog is for educational purposes, based on personal study, industry cases, and exporter experiences. Always consult your bank before finalizing any LC transaction.